NASA announced Hubble's discovery of the farthest and one of the oldest stars ever seen, Earendel. The star took 12.9 billion years to be in closer proximity to Earth.
Hubble's new discovery appears to provide a remarkable glimpse into the early universe.
As reported by NASA, the Hubble Space Telescope has set a new record-breaking discovery for astronomy by detecting the light of this star that existed within the first billion years after the universe's creation in the big bang - the farthest individual star ever observed to date.
The light from the star Earendel has traveled an estimated 12.9 billion years to reach the Earth — a significant increase in distance from the previous most distant star. Detecting the star was made possible by a rare star alignment.
The previous title holder in star discovery was held by the star named Icarus, recorded to have taken 9 billion years to reach Earth.
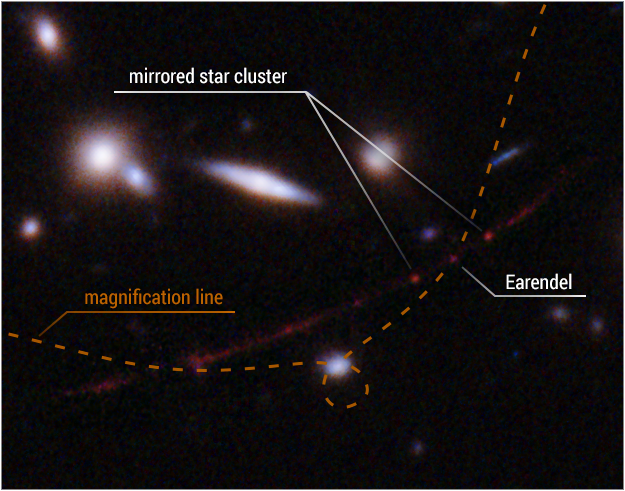
A detailed view of Earendel's position as seen from the Hubble Telescope.
Earendel's Discovery
Earendel is estimated by scientists to be at least 50 times the mass of the Sun and millions of times as bright, placing it among the most massive stars known. Earendel comes from an Old English name that means "morning star".
However, the Hubble space observatory has identified Earendel as a distinct object by taking advantage of a natural phenomenon that is analogous to using a zoom lens.
As reported by BBC, "It's called gravitational lensing and it works like this: If there is a great cluster of galaxies in the line of sight, the gravitational pull from this mass of matter will bend and magnify the light of more distant objects behind."
Normally, this is due to the presence of other galaxies. But in this particular instance, Earendel was in an ideal range in terms of the lens effect.
In a NASA exclusive, Brian Welch, an astronomy Ph.D. student from Johns Hopkins University stated that: "We almost didn't believe it at first, it was so much farther than the previous most-distant, highest redshift star.. Normally at these distances, entire galaxies look like small smudges, with the light from millions of stars blending together. The galaxy hosting this star has been magnified and distorted by gravitational lensing into a long crescent that we named the Sunrise Arc."
"Studying Earendel will be a window into an era of the universe that we are unfamiliar with, but that led to everything we know."
Learning about Earendel will provide a window into a period of the universe that humans are unfamiliar with but which was also crucial in the development of every known thing in the world.
Read Also: NASA Will Take Your Name on a Trip Around the Moon
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope
Scientists anticipate that Earendel will continue to be magnified at a high level for many years to come. However, NASA reports that the James Webb Space Telescope will be the one to confirm if Earndel is indeed a star.
Dan Coe of the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) stated that scientists expect Webb to be able to confirm that Earendel is, in fact, a star, as well as to measure its brightness and temperature.
Astronomer Brian Welch added that Webb may be able to see stars even further away than Earendel, an incredibly exciting possibility for astronomy.
Related Article: NASA's Space Launch System Rollout a Success! Next Stop: The Moon