Generative AI systems have become essential to how teams communicate and create, yet challenges with their short-term memory capabilities remain a major obstacle to greater adoption by startups and corporates alike. Tanka, a fast-growing AI startup, has introduced a new solution: EverMemOS, an AI-native × memory-native operating system designed to give intelligent agents persistent memory across the tools people already use.
Unlike conventional chat-based assistants that forget context once a session ends, EverMemOS maintains a continuous thread of understanding across platforms such as Slack, Gmail, Notion, and WhatsApp. The result, according to the company, is an AI layer that can recall past discussions, track progress, and assist teams with follow-ups and summaries, thereby bridging a long-standing gap between human collaboration and digital automation.
Tanka's approach echoes a broader shift in the AI industry, where developers are increasingly exploring long-term context retention as the next leap in productivity and reliability. The system's "memory-native" design allows it to connect chats, files, and workflows into one searchable context engine. Within this layer operates a built-in assistant that can automatically generate recaps, identify pending actions, and retrieve relevant materials within seconds.
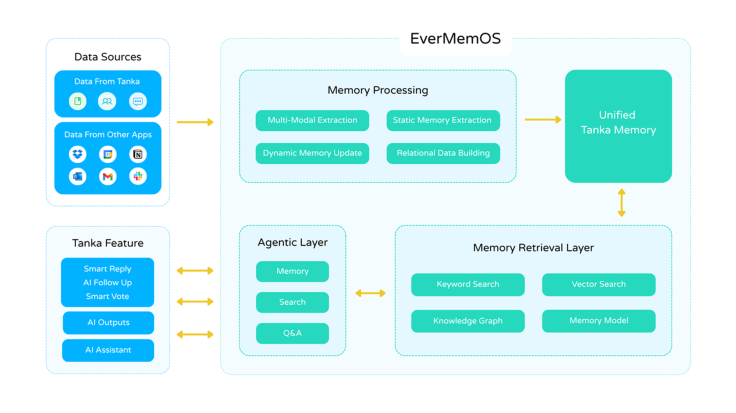
EverMemOS operates through a multi-layered architecture that mirrors how human memory organizes and retrieves information, according to information provided by Tanka.
As shown in the diagram, data flows from everyday apps like Slack, Gmail, and Notion into a Memory Processing unit that performs multimodal extraction, dynamic updates, and relational data building. These elements feed into a Unified Tanka Memory, which in turn powers two functional layers—the Agentic Layer (responsible for actions like Q&A and follow-ups) and the Memory Retrieval Layer (handling keyword, vector, and knowledge-graph searches).
This structure allows EverMemOS to store and recall information across tools while maintaining a single coherent context, providing a key differentiator from traditional, stateless LLM assistants.
In early use cases, Tanka has tested the platform through a Fundraising Agent tailored for startup teams. This agent leverages stored memory to help founders prepare investor decks, track meeting questions, and manage follow-ups without re-entering prior data, streamlining a process that traditionally demands hours of manual coordination and locks up team members' time.
To validate its architecture claims, Tanka reports that EverMemOS scored 92.3% on LOCOMO, a new benchmark for long-context memory performance. While benchmarks for "memory" are still evolving, this result suggests a competitive edge in retaining and retrieving multi-session information—a feature many AI systems still lack.
Tanka plans to open-source EverMemOS, encouraging developers to build their own memory-native agents atop the platform. If adopted widely, this could mark a turning point for AI productivity tools, transforming how information flows between applications and how teams retain knowledge over time.
As the debate around persistent AI memory grows—balancing personalization, privacy, and performance—EverMemOS presents one of the most structured attempts to operationalize memory within daily workflows to date. Its success may signal how the next generation of AI systems will not just respond to users, but remember them.









