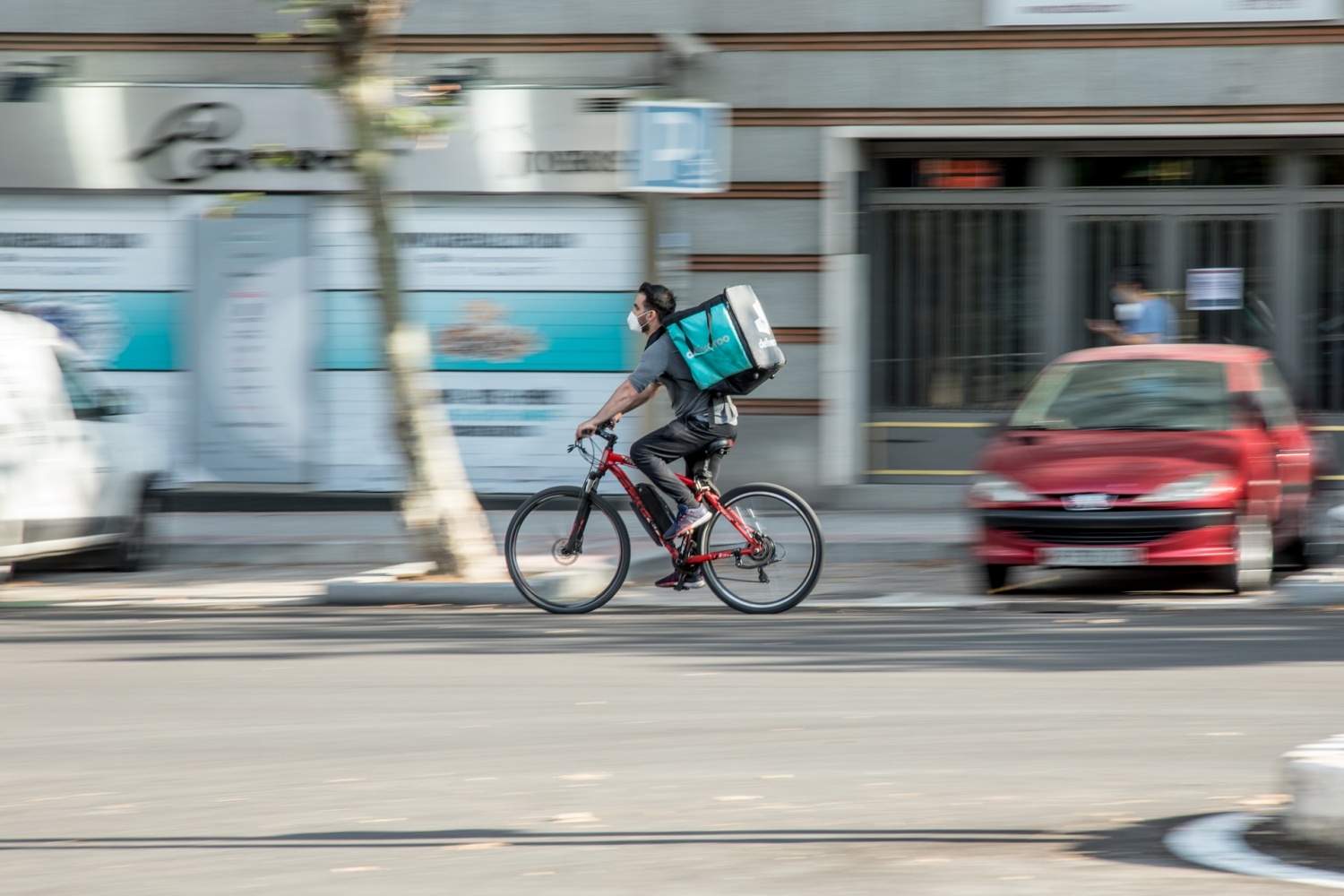
The growing rise of e-commerce and package delivery worldwide necessitates the development of new solutions to meet customers' demands for more and faster deliveries. Fresh driverless air and ground vehicles are being developed and tested to deliver goods and services in retail, grocery, and healthcare.
Most importantly, setting clear sustainability targets that incorporate a more environmentally-friendly last mile is a vital step in combating climate change. Companies like Smartroutes promote sustainability through their delivery management software.
Last-mile is the ugliest part of the supply chain
Customer expectations regarding their delivery experiences have transformed the way firms approach their delivery and fulfillment operations. Customers want full visibility on their orders as they make their way to them, they want super-fast delivery and they want it for free.
While meeting these expanding expectations is becoming increasingly difficult for businesses, improving route optimization and driving long-term, sustainable growth is critical.
What exactly is the last mile problem?
The primary concern in the final mile is the expense. Because the last mile accounts for 50% of overall transportation expenses, shipping companies must impose surcharges. Simultaneously, shippers must pass on some of the delivery costs to customers, a strategy that may jeopardize their appeal in the massive and competitive retail and eCommerce marketplaces.
Challenges faced by last-mile logistics:
-
Increasing supply chain visibility and data
This critical component of any delivery operation is current data on the exact location of orders and related inventory. It is also the number of open orders from each eCommerce site, the corresponding internal processes, and the internal or external fleets available to make the deliveries.
Businesses will get critical insights into optimizing delivery operations by having data on the delivery flow and consumer data. These advancements will allow organizations to provide the speed, flexibility, and convenience that their customers expect.
-
Multi-fleet management and crowdsourced fleet management
Businesses that rely on fleets other than their own confront a distinct set of issues that must be addressed. This is especially important given that external delivery employees are the ones that make the vital final mile contact with customers.
Businesses that use several crowdsourced fleets must discover ways to keep complete control over the entire delivery process to meet their business objectives for branding and quality of service. Only by maintaining this level of control will they meet and surpass their customers' delivery expectations.
-
Creating and maintaining numerous delivery models while keeping costs under control
While delivery companies must improve their customers' delivery experiences, they must also cut related expenses to retain a good ROI. While scaling and expanding to offer a range of delivery models (scheduled, on-demand, etc.) causes a slew of issues throughout the delivery ecosystem.
Taking delivery management seriously
To enable cost-effective same-day delivery, one option is Continuous Delivery, that is the capacity to constantly add parcel collections and deliveries to a driver's route throughout the day. For example, a driver might begin their day by picking up 16 packages at a local fashion store, then deliver 10 parcels to local clients before picking up an extra 8 packages at a local general retail store.
This continuous strategy will increase route density, improve fleet utilization, and lower delivery costs. Carriers must utilize four critical characteristics to allow Continuous Delivery and meet consumer demand for faster, more flexible delivery:
-
Advance Forecasting:
Intelligent algorithms are utilized to anticipate collection and delivery locations and order time. These projected orders are fed into the route optimization engine, which uses them to enhance driver response times, boost collections and deliveries on each route, and lower transportation costs.
-
Delivery Optimization:
Dynamic route optimization is used to optimize and re-optimize routes throughout the day to respond to and arrange incoming collections and deliveries across the network promptly and efficiently. This keeps drivers on a more efficient path while also allowing them to adapt quickly to changes during the day by exploiting real-time data.
-
Insightful observations:
Machine learning and sophisticated analytics skills will be used to assess delivery performance and suggest possibilities to improve route density and delivery efficiency. These can include extra features that provide merchants with enhanced transparency over the end-to-end delivery process, allowing them to monitor carrier performance and choose the best delivery choice among their possibilities.
-
Real-Time Tracking:
Customers have gained visibility and control over the end-to-end delivery experience by using real-time tracking GPS breadcrumbs and scan events. This includes real-time tracking and tracing, delivery notifications, adjustable delivery windows, and direct connection with the delivery driver or customer service representative. These real-time customer updates, along with all real-time data updates, are then pushed back into the route optimization engine.
-
Autonomous Vehicles and Drone Deliveries:
Last-mile delivery and logistics solutions can be extremely useful in enabling future-ready and revolutionary technology. Smart firms have already begun testing self-driving vehicles by delivering food on college campuses.
Also, fast-food companies use drone technology to provide food to customers through their balconies and windows. It won't be long before robot experiments are launched as well.
Improving Delivery Management:
Delivery management is all about process optimization, whether you're a tiny business just getting started or a multinational conglomerate. Delivery operations continuously attempt to reduce costs by completing more deliveries with fewer resources (person-hours, cars, fuel) while still providing excellent customer service. Delivery managers use various tools and tactics to improve their KPIs and scale up their operations.
1. Improve your route planning:
Route optimization is an essential aspect of delivery management. You can send items quickly and affordably if you have the correct technology in place to find the most efficient route. With the help of delivery management software you can plan your journeys fast and effortlessly.
2. Automated dispatch:
Running a large-scale, on-demand delivery service necessitates some degree of automation of the dispatching process. Unlike planned deliveries, which can benefit from forward-thinking route optimization, on-demand firms must be prepared to dispatch fresh orders on the fly.
Automating dispatch frees up a delivery manager's valuable time, allowing them to focus on addressing exceptions and assuring customer satisfaction.
3. Use Route Management Software:
The most incredible method to improve the efficiency of your delivery operations is to employ route management software. This program includes the capabilities you need to streamline your deliveries and optimize the delivery path. This technique ensures that deliveries are completed on time and allows you to plan the route to save fuel and time.
You no longer have to go back and forth to accomplish your deliveries by coordinating the delivery depending on a specified area. You can get real-time information on route optimization software of traffic statistics and road incidents, allowing you to plan an alternate route while you drive.
4. Reducing liability expenses:
By tracking the parameters of your fleet and the conduct of your drivers, businesses may typically cut insurance prices by sending this data to their brokers.
5. Communication within the team and with customers:
The dispatchers would assign jobs to the drivers, who would then complete them. However, in the real world, it is vital to foster fluid communication among team members. When a driver is having trouble finding a dropoff location or contacting a customer, the first call they normally make is to their dispatcher for assistance. This instruction is an essential aspect of the delivery management process.
Key Takeaways:
In this article, we have discussed the last mile problem and the challenges faced by last-mile logistics. Then we saw why we should take delivery management seriously and improve the delivery management system.